How to Use Moogle Math ?
Welcome to the ultimate guide on how to get the most out of Moogle Math! This page is designed to ensure you fully understand how to navigate, interact, and utilize all the features of this powerful platform. Whether you’re solving math problems, exploring physics, or diving into chemistry, Moogle Math is here to assist every step of the way.
How to Use Moogle Math Effectively
Remember, Moogle responds intelligently base on how you query it.
1. Start with a Query
Type your question or problem into the input box.
- Solve for x in 2x + 3 = 7
- What is Newton’s second law?
- Factorize x^2-5x+6
Once you submit your query, Moogle Math will analyze it and provide:
- A step-by-step solution.
- Explanations of concepts and formulas used.
2. Explore Specific Subjects
To explore additional subjects, click on the “Change the Subject” link and unlock access to over 100 more topics across diverse fields.
- Mathematics: Algebra, Calculus, Probability, and more.
- Physics: Mechanics, Electromagnetism, Quantum Physics, and beyond.
- Chemistry: Organic, Inorganic, and Physical Chemistry.
- Biology: Molecular Biology, Genetics, and Evolution.
- Computer Science: Algorithms, Machine Learning, Cybersecurity, and more.
- Engineering: Civil, Mechanical, Electrical, and Chemical Engineering.
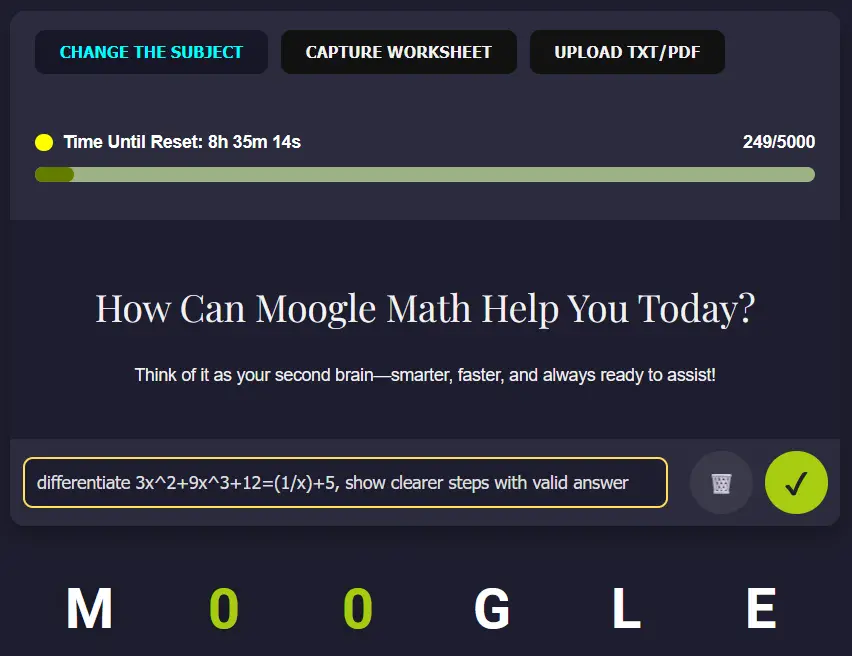
3. Step-by-Step Solutions
Each problem is broken down into clear, manageable steps so you can:
- Follow the logic and reasoning.
- Learn why and how each step is applied.
- Master the approach to solving similar problems on your own.
4. Learn Key Concepts
If you need help understanding a concept, ask directly. Moogle Math will provide detailed yet simple explanations using:
- Definitions of terms.
- Real-life examples to make concepts relatable.
- Diagrams and formatted equations for clarity.

Query Formation Matters!
📢 Important Reminder: To get the most accurate and reliable answers from Moogle Math, it’s essential to ensure your queries are clear and properly formed.
If a query is vague, incomplete, or incorrectly structured, Moogle may return unexpected or less helpful results. For the best experience, follow these tips:
Be Specific
Instead of asking, “Solve this equation,” provide the full equation, like “Solve 2x + 5 = 15.”
Use Standard Symbols:
Use clear mathematical notation like +,-,/,*,^, and parentheses ( ) to avoid confusion.
Avoid Ambiguity
If your problem involves steps or context, explain it briefly. For example:
Correct: “Find the derivative of f(x) = 3x^2.”
Incorrect: “Find the derivative of the function
Capturing Worksheets and Uploading Expressions
Moogle provides premium-level support for free, making it a standout platform in the educational and professional assistance space. It offers:
5. Capturing Worksheets
Moogle Math allows you to save and use worked-out solutions with ease. By clicking the “Capture Worksheet” button, you can take a snapshot of the worked expressions provided by Moogle. This feature is perfect for storing solutions for future reference, sharing with others, or integrating them into your study materials.
6. Uploading Expressions from TXT or PDF Files
Got a complex mathematical or scientific query in a document? Moogle Math supports direct uploads of expressions from TXT or PDF files. Simply upload your file, and Moogle will extract and process the mathematical expressions for a seamless problem-solving experience.
This makes Moogle Math not just an interactive problem solver but also a highly versatile tool for academic and professional use.
Querying Moogle The Right Way
Moogle provides premium-level support for free, making it a standout platform in the educational and professional assistance space. It offers:
Sample Queries for Moogle Math
Here are additional queries across various subjects formatted for mathematical and scientific expressions:
Mathematics Queries
1. Evaluate the integral: \( \int_0^2 (3x^2 + 2x) \, dx \).
2. Solve a quadratic equation: \( x^2 – 5x + 6 = 0 \).
3. Find the sum of a geometric series: \( S_n = \frac{a(1 – r^n)}{1 – r}, \, a = 2, \, r = 3, \, n = 4 \).
Physics Queries
1. Calculate work done: \( W = Fd\cos\theta, \, F = 10 \, \text{N}, \, d = 5 \, \text{m}, \, \theta = 30^\circ \).
2. Determine kinetic energy: \( KE = \frac{1}{2}mv^2, \, m = 2 \, \text{kg}, \, v = 3 \, \text{m/s} \).
3. Calculate the period of a pendulum: \( T = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{L}{g}}, \, L = 0.5 \, \text{m}, \, g = 9.8 \, \text{m/s}^2 \).
Chemistry Queries
1. Determine molar mass: Find the molar mass of \( \text{H}_2\text{SO}_4 \).
2. Calculate molarity: \( M = \frac{n}{V}, \, n = 0.5 \, \text{mol}, \, V = 0.2 \, \text{L} \).
3. Determine energy change in a reaction: \( \Delta H = \Sigma H_{\text{products}} – \Sigma H_{\text{reactants}}, \, H_{\text{products}} = -200 \, \text{kJ}, \, H_{\text{reactants}} = -100 \, \text{kJ} \).
Biology Queries
1. Analyze photosynthesis: Write the balanced equation for photosynthesis: \( 6\text{CO}_2 + 6\text{H}_2\text{O} \xrightarrow{\text{light}} \text{C}_6\text{H}_{12}\text{O}_6 + 6\text{O}_2 \).
2. Classify DNA bases: Which bases pair in DNA: \( \text{A-T, G-C} \)?
3. Population growth: Calculate population size using \( P = P_0e^{rt}, \, P_0 = 100, \, r = 0.05, \, t = 5 \).
Computer Science Queries
1. Sort an array: Write a step-by-step example to sort \( [5, 2, 8, 1, 3] \) using bubble sort.
2. Binary search: Search for \( 7 \) in the array \( [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] \).
3. Evaluate complexity: What is the time complexity of \( \text{merge sort} \)?
Economics Queries
1. Find equilibrium price: Given \( Q_d = 100 – 2P \) and \( Q_s = 20 + 3P \), solve for \( P \).
2. Interest rate calculation: \( FV = PV(1 + r)^t, \, PV = 1000, \, r = 0.05, \, t = 10 \).
3. Profit calculation: \( \pi = TR – TC, \, TR = 2000, \, TC = 1500 \).
Engineering Queries
1. Stress and strain: Calculate stress: \( \sigma = \frac{F}{A}, \, F = 500 \, \text{N}, \, A = 0.01 \, \text{m}^2 \).
2. Thermal expansion: \( \Delta L = \alpha L_0 \Delta T, \, \alpha = 1.2 \times 10^{-5}, \, L_0 = 2 \, \text{m}, \, \Delta T = 50^\circ \text{C} \).
3. Hydraulic system pressure: \( P = \frac{F}{A}, \, F = 1000 \, \text{N}, \, A = 0.02 \, \text{m}^2 \).
Psychology Queries
1. Cognitive load: Explain how working memory processes \( 5+/-2 \) chunks of information.
2. Freudian theory: How does the \( \text{id, ego, and superego} \) influence behavior?
3. Behavioral conditioning: Illustrate classical conditioning using Pavlov’s dog experiment.
Sociology Queries
1. Social structure: Define the concept of \( \text{class stratification} \).
2. Urban sociology: What factors contribute to \( \text{urban sprawl} \)?
3. Research methods: Compare \( \text{quantitative} \) and \( \text{qualitative} \) sociology.
These queries are designed for demonstration and to provide real-world context for using Moogle Math effectively.
What Happens with Improper Queries?
Moogle might interpret your input differently, resulting in
Wrong answers
Incomplete Answers: Missing steps or assumptions.
Bad Results
Inaccurate Results: Incorrect interpretation of the problem.
Mismatch response
Ambiguous Outputs: Solutions that may not match your intent.
🛠 Need Help?
If you’re unsure how to phrase your query, ask Moogle for guidance:
Example: “How should I format my query to solve a quadratic equation?“